Salesforce Collections Basics
Hi Developers !!. This post is regarding the Salesforce Data Collections. Before going into details we need to know what are Data Collections. So here we go :
Examples
Now open Logs and Click on Debug Only. You will find the below result.
Set Methods
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
How to use Set in Trigger Context - Please find the below snippet of code.
Lists
Examples
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
List Methods
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
Data Collections - As the name suggests, Data Collections are simply grouping of any Data Types.
Data Collections in Salesforce - Apex Collections or Salesforce Collections has Three different types of Collections or we can say the Apex Language provides Developers with three different types of Classes where we can store our data in any one of these classes. The classes are:
1. Sets
2. Lists
3. Maps
We use the above Apex Collections often in our Triggers, Controllers and Classes because they go hand in hand with SOQL (Salesforce Object Query Language)
All these Collections works like an ARRAY with Some additional features which Salesforce provides us and have easier access methods than ARRAY.
Why we Need Apex Collections ?
There are many Limitations with APEX programming. Out of which some are related to DML Operations such as Number of rows retrieved , Limits on number of DML's etc. For these reasons we need to be good in Apex collections. Otherwise we may run into Governor Limits Errors.
Sets
A Set is a collection of UNIQUE and UNORDERED Elements. By the word UNIQUE I mean Sets will never allow any duplicate value. It can contains Primitive Data Types such as Integers, Date, Strings, Sobjects and so on.
When we need Sets ?
When we want to use data without duplicate values in our SOQL query. For Example : we need to store collections of Ids in Set.
Syntax
To create a Set we need to use the new Keyword and we need to use the Set keyword followed by the Primitive data type contained in the Characters ( <> )
Set <String> str = new Set <String> ( ) ;
Set <String> str = new Set <String> {'Hello', 'This', 'Is', 'A', 'Set'} ;
In the above Set Syntax - Set is a keyword .
String is a Data Type .
Str is an object.
New is a keyword which will initialize Set.
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
Behaviour with Sobjects -
As we know, Sets does not contain Duplicate values. So, In Salesforce Sets find the uniqueness of data based upon fields. For Example :
Account acc = new account (Name = 'XYZ') ;
Account acc1 = new account (Name = 'XYZ') ;
Set <Account> c = new Set <Account> {acc, acc1} ;
In the above Set, The Set will contain only one Value because both Accounts have same name
and the size of set will be 1.
and the size of set will be 1.
Account acc = new account (Name = 'XYZ') ;
Account acc1 = new account (Name = 'XYZ' , Description = 'New Account') ;
Set <Account> accSet = new Set <Account> {acc, acc1} ;
In the above Set, The Set will contains Two Values and the size will be 2.
Try it Yourself -
Go to Developer Console and paste the below piece of Code.
Now open Logs and Click on Debug Only. You will find the below result.
Set Methods
There are different types of Set Methods. Each method has its own unique Properties. The methods are :
1. add(Object)
2. addAll(List<Object>)
3. addAll(Set<Object>)
4. clear( )
5. clone( )
6. contains(Object)
7. containsAll(List<Object>)
8. containsAll(Set<Object>)
9. equals(Set<Object>)
10. hashCode( )
11. isEmpty ( )
12. remove(Object)
13. removeAll(List<Object>)
14. removeAll(Set<Object>)
15. retainAll(List<Object>)
16. retainAll(Set)
17. Size( )
For further information regarding the above methods you can go to below link :
Lets Play with some of the Set Methods. Paste the below Snippet of Code and See the Results !!
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
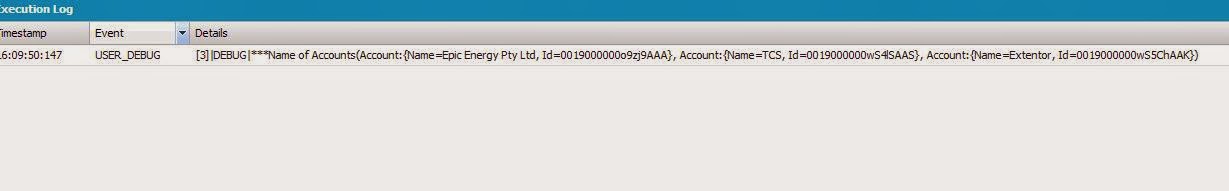
How to use Set in Trigger Context - Please find the below snippet of code.
Set<ID> ids = new Set<ID>{'0019000000o9zj9', '0019000000wS5Ch', '0019000000wS4lS'};
List<Account> acc = [Select Name from Account where ID = : ids];
System.debug('***Name of Accounts'+ acc);
Lists
A List is a collection of elements, such as Integers, Strings, Objects and so on which allow Duplicates.We use List when the sequence of elements is important. It is very much similar to ARRAY.List is a Collection of Ordered Elements. As Arrays are Zero based similarly Lists are also Zero based.The first element in List is always at 0th Index and the last element will be at (n-1) index.
Syntax
To create a Set we need to use the new Keyword and we need to use the Set keyword followed by the Primitive data type contained in the Characters ( <> )
List <String> str = new List <String> ( ) ;
List <String> str = new List<String> {'Hello', 'This', 'Is', 'A', 'Set'} ;
In the above List Syntax - List is a keyword .
String is a Data Type .
Str is an object.
New is a keyword which will initialize Set.
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
Behaviour with Sobjects -
As we know, Sets can contains Duplicate values.
Account acc = new account (Name = 'XYZ') ;
Account acc1 = new account (Name = 'XYZ') ;
List<Account> c = new List <Account> {acc, acc1} ;
In the above List, The List will contains Two Values and the size will be 2.
Why Lists are important ?
The reason why Lists are important is because the output of every SOQL query is a LIST. The main characteristic of List is they are ordered , So we can get the specific element of our List by the element's index.
Try it Yourself -
Go to Developer Console and paste the below piece of Code.
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
List Methods
There are different types of List Methods. Each method has its own unique Properties. The methods are :
1. add(Object)
2. add(Integer,Object)
3. addAll(List)
4. addAll(Set)
5. clear( )
6. clone( )
7. deepClone(Boolean,Boolean,Boolean)
8. equals(List)
9. get(Integer)
10. getSobjectType( )
11. hashCode( )
12. isEmpty( )
13. iterator( )
14. remove(Integer)
15. set(Integer, Object)
16. size( )
17. sort( )
For further information regarding the above methods you can go to below link :
Lets Play with some of the List Methods. Paste the below Snippet of Code and See the Results !!
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
How to use List in Trigger Context - Please find the below snippet of code.
List<String> ids = new List<String>{'0019000000o9zj9', '0019000000wS5Ch', '0019000000wS4lS', '0019000000wS5Ch'};
List<Account> acc = [Select Name from Account where ID = : ids];
System.debug('***Name of Accounts'+ acc);
Maps
A Map is a collection of key-value pairs. Keys can be any primitive data type. Values can include primitive data types, as well as objects and other collections. Use a map when finding something by key matters.
You can have duplicate values in a map, but each key must be unique. Maps are used when we want to store records which process or as containers for lookup data.
You can have duplicate values in a map, but each key must be unique. Maps are used when we want to store records which process or as containers for lookup data.
Syntax
To create a Map we need to use the new Keyword and we need to use the Map keyword.
Map<Integer, String> ma = new Map <Integer, String> {1 => 'xyz', 2 => 'abc', 3 => 'kjh'};
Map<ID, Set<String>> ma = new Map<ID, Set<String>>( );
// Map where key is the id of the record
Map<Id, Account> accMap = new Map<Id, Account>([select id, Name from Account LIMIT 2]);
In the above Map Syntax - Map is a keyword .
New is a keyword which will initialize Map
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
Map Methods
The values are passed in the curly braces { }.
Map Methods
There are different types of Map Methods. Each method has its own unique Properties. The methods are :
1. clear( )
2. clone( )
3. ContainsKey(Object)
3. ContainsKey(Object)
4. deepClone( )
5. equals(Map)
6. get(Object)
7. getSobjectType( )
8. hashCode( )
9. isEmpty( )
10. KeySet( )
11 put(Object, Object)
12 putAll(Map)
13. remove(Key)
14. size( )
15. values ( )
For further information regarding the above methods you can go to below link :
15. values ( )
For further information regarding the above methods you can go to below link :
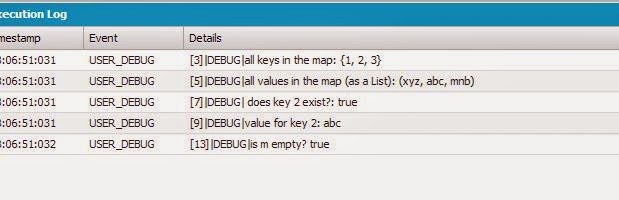
Lets Play with some of the Map Methods. Paste the below Snippet of Code and See the Results !!
Result - Open Logs and Click on Debug only.
Maps are also used extensively to stay within Governors and Limits.
Difference between oldMap and newMap ?
The oldMap Contains a list of sObject before they were modified and newMap contains a list of sObject with the updated values. we use these Maps to make some comparison inside the trigger.
Example
for(Id id : Trigger.newMap.keySet()) {
If(Trigger.oldMap.get(id).LastName != Trigger.newMap.get(id).LastName){
System.debug('++ last name has been Changed');
}
}
Enjoy Coding !!!









Great Stuff
ReplyDeleteGood stuff bavesh
ReplyDelete